How to check if your computer is Hyper V enabled
Second Level Address Translation is a technology introduced in both Intel and AMD flavours of processors. Both companies call their version of the technology different names, Intel’s version is called EPT(Extended Page Tables) and AMD calls theirs RVI (Rapid Virtualization Indexing). Intel introduced Extended Page Tables in its processors that were built on the Nehalem architecture, while AMD only introduced RVI in their third generation of Opteron processors codenamed Barcelona. Hyper-V uses this to perform more VM memory management functions and reduce the overhead of translating guest physical addresses to real physical addresses. By doing this, Hypervisor CPU time is significantly reduced, and more memory is saved for each VM.
To find out if your processor supports SLAT, you will need to download a copy of CoreInfo(see link at end). Once you have downloaded it you will need to extract it. You should extract it so that coreinfo is in the root of your C:\ drive.
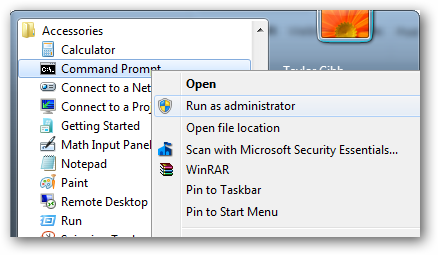
You will need to open an elevated command prompt, read “run as administrator”.
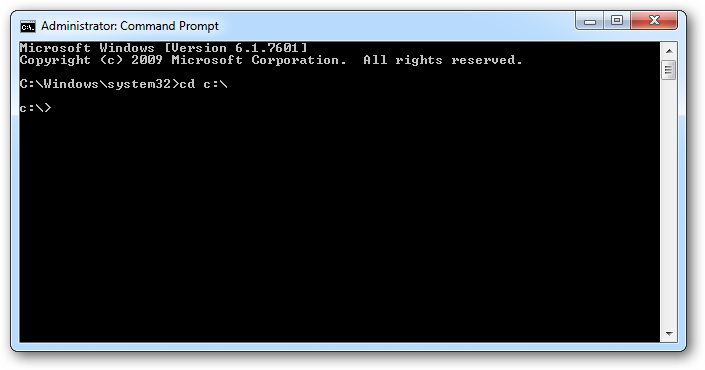
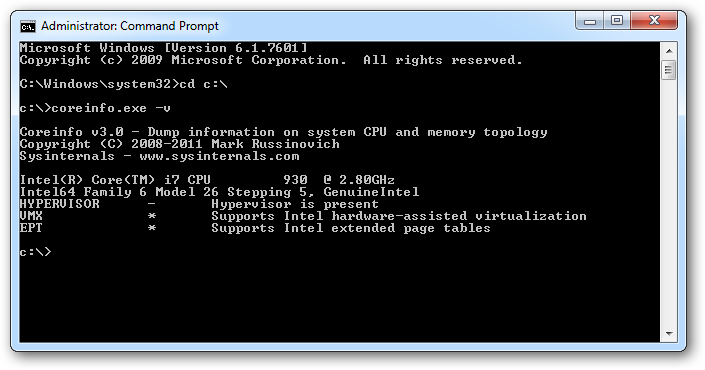
To see if your processor supports SLAT you will need to run “coreinfo.exe -v”. On an Intel if your processor supports SLAT it will have an asterix in the EPT row. This is seen in the screenshot below.
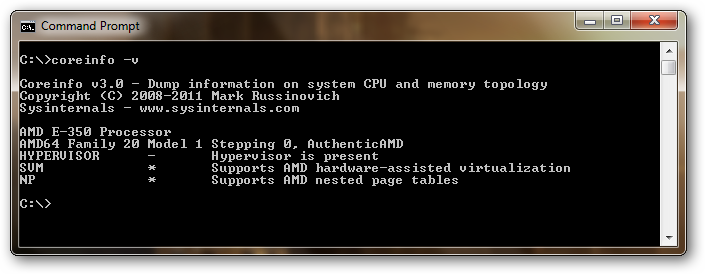
On an AMD if your processor supports SLAT it will have an asterisk in the NPT row.
If your processors don't support SLAT you will see a dash in the EPT or NPT rows.
Comments
0 comments
Please sign in to leave a comment.